What is HPV in the Throat?
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common virus. Some strains (especially HPV-16) can infect the throat through oral contact and, in a small number of people, cause long-term changes.
Most HPV infections:
-
Cause no symptoms
-
Clear on their own within 1–2 years
-
Never lead to serious disease
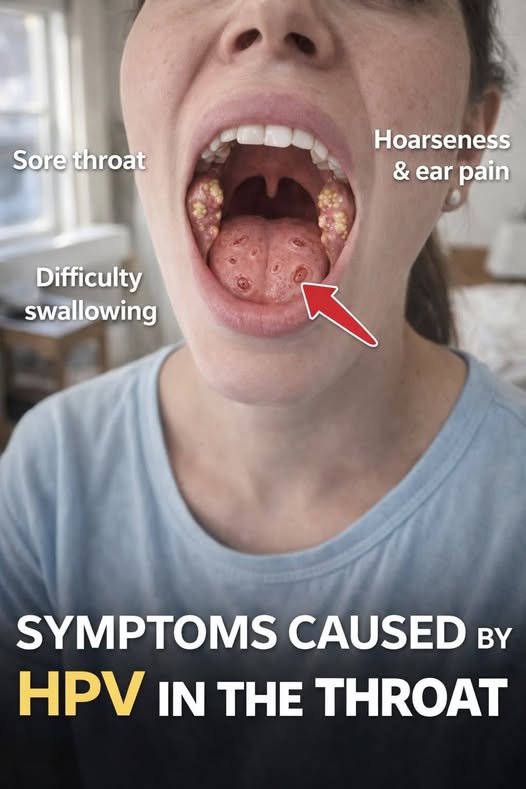
Common Symptoms
Many people have no symptoms at all, but when symptoms occur, they may include:
-
Persistent sore throat
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Hoarseness or voice changes
-
Ear pain (without ear infection)
-
A lump sensation in the throat
-
Swollen tonsils or neck lymph nodes
-
Unusual bumps or lesions in the mouth or throat
-
Unexplained weight loss (later stages – rare)
⚠️ Symptoms lasting more than 2–3 weeks should be checked by a doctor.
Is HPV in the throat cancer?
Not automatically.
-
Most HPV throat infections are harmless
-
A small percentage can progress over many years into oropharyngeal cancer
-
HPV-related throat cancers often respond very well to treatment when caught early
How It’s Diagnosed
There is no routine screening test for throat HPV.
Doctors may use:
-
Physical examination
-
Throat endoscopy
-
Biopsy of suspicious lesions
-
Imaging (CT, MRI) if needed
Treatment & Solutions
✔️ If there are NO serious symptoms
-
Monitoring only
-
The immune system often clears the virus naturally
✔️ If symptoms are present
-
Treat pain or inflammation
-
Voice therapy (for hoarseness)
-
Removal of warts or lesions if needed
✔️ If cancer develops (rare)
-
Surgery
-
Radiation
-
Chemotherapy
(HPV-related throat cancers generally have high survival rates)
Prevention (Very Important)
-
HPV vaccine (Gardasil 9) – highly effective
-
Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol
-
Practice safer oral sex
-
Maintain good oral hygiene
-
Regular dental and medical checkups
The HPV vaccine protects against the strains most likely to cause throat cancer.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you have:
-
Throat symptoms lasting over 2–3 weeks
-
Pain when swallowing
-
Persistent ear pain on one side
-
A lump in the neck
-
Bleeding or unexplained sores
Common Q & A
Q: Can HPV in the throat go away on its own?
Yes. Most infections clear naturally.
Q: Is it contagious?
Yes, through oral contact, but it’s extremely common and usually harmless.
Q: Should I be scared?
No. Awareness is important, panic is not. Early evaluation = excellent outcomes.
Q: Can vaccinated people still get it?
Risk is much lower, but no vaccine is 100%.